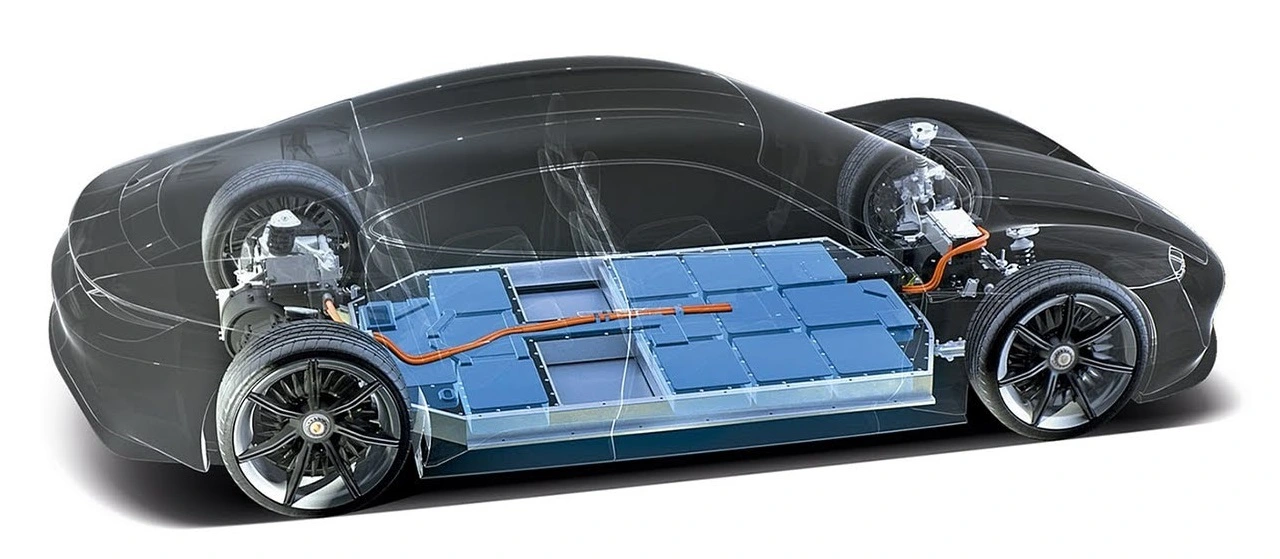
Table of Content
▼Electric vehicles have steadily been gaining in popularity. As more manufacturers develop and launch new models, it's easy to envision an all-electric future. But the key to an electric car's success is their range, which is heavily dictated by their battery capacity. How is all that power stored? Electric car batteries have to be compact, capable of recharging quickly and regularly, and also house plenty of power to take you anywhere you want.
This article explores the most common types of electric vehicle batteries, their potential capacity, and and how long they typically last.
What type of batteries do electric cars use?
There have been many advancements in battery technology over the past 40 years. With the push towards more sustainable energy, we've come a long way from the lead-acid batteries of the past. Let's take a look at the two most common types of batteries used in electric vehicles today.
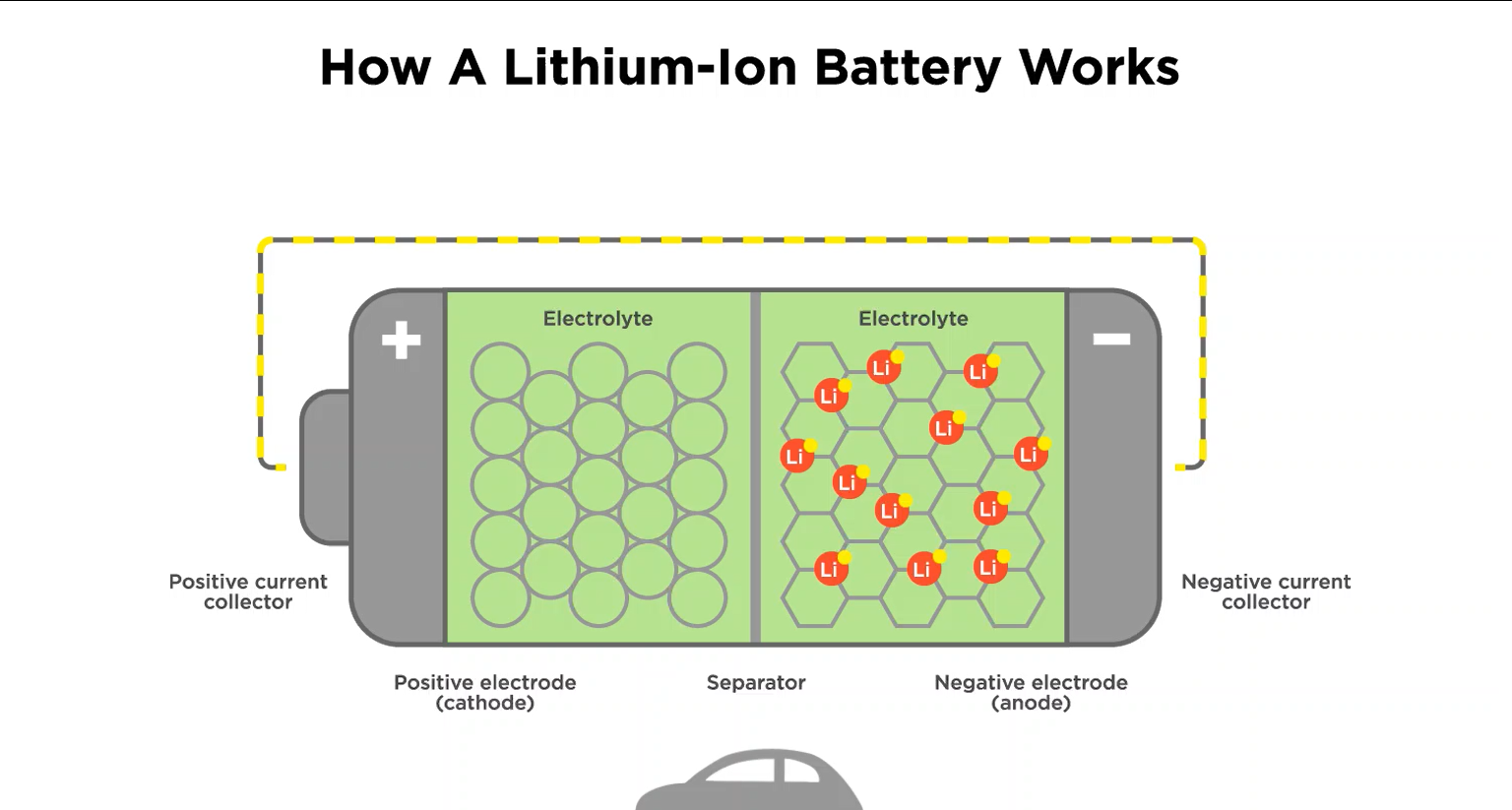
Lithium-ion batteries
Most new electric cars feature lithium-ion batteries. There are 6 main chemical types of lithium, and cars tend to use the types with the highest energy density. This is usually lithium cobalt oxide (LCO) or lithium nickel cobalt oxide (NCA).
When it comes to cell housing, there are three different types: cylindrical, prismatic, and pouch-type batteries. You'll find all three in electric cars today, and each one has pros and cons.
For example, Tesla chooses to use cylindrical batteries for their reliability and durability. Their battery packs contain hundreds of lithium-ion cells stored beneath the vehicle's interior. In fact, the Tesla contains 2,976 lithium-ion battery cells. These lithium-ion battery cells are the highest energy-density battery in the world. Nevertheless, they’re cumbersome compared to other types.
Like cylindrical batteries, prismatic feature a solid casing; However, prismatic batteries are generally lighter and fit well into small spaces due to their rectangular shape. For this reason, Volkswagen recently switched to prismatic batteries. However, prismatic batteries typically have a shorter cycle life than cylindrical batteries.
Pouch batteries differ because they’re in thin, metal bags, making them more flexible than prismatic and cylindrical batteries. Because of this, they are fantastic for small, oddly shaped spaces, but they can be vulnerable to swelling and pose a potential fire risk. Both GM and Hyundai use pouch-type batteries.
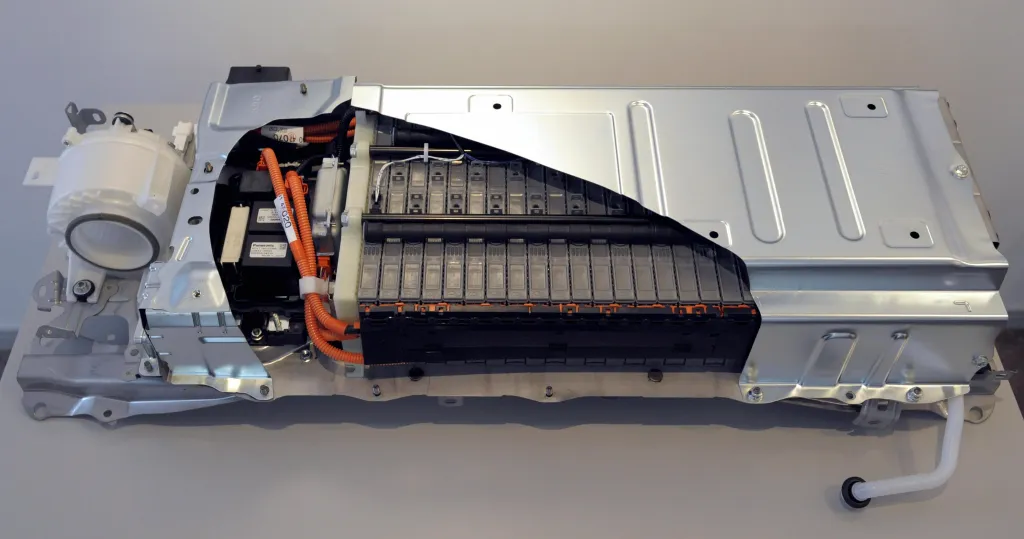
Nickel-metal hybrid batteries
Created in 1987, nickel-metal hybrid batteries, paved the way for hybrid vehicles. This happened with the invention of a new cathode material made of lanthanum, nickel, cobalt and silicon. The new formula helped the cell retain 84% of its charging capacity, even after 4,000 charge/recharge cycles.
Later, more advances in battery chemistry helped nickel-metal hybrid batteries retain much more energy density than lead-acid batteries.
You'll now find nickel-metal hybrid batteries mainly in hybrid cars. They are popular because of their high energy output and safety. Additionally, like lithium, a battery's state of charge does not affect its output as much as lead-acid.
However, nickel-metal hybrid batteries are expensive. They also have high self-discharge rates and higher cooling requirements. You'll find this type of electric car battery in the Toyota Prius, Honda Insight, and Civic Hybrid.
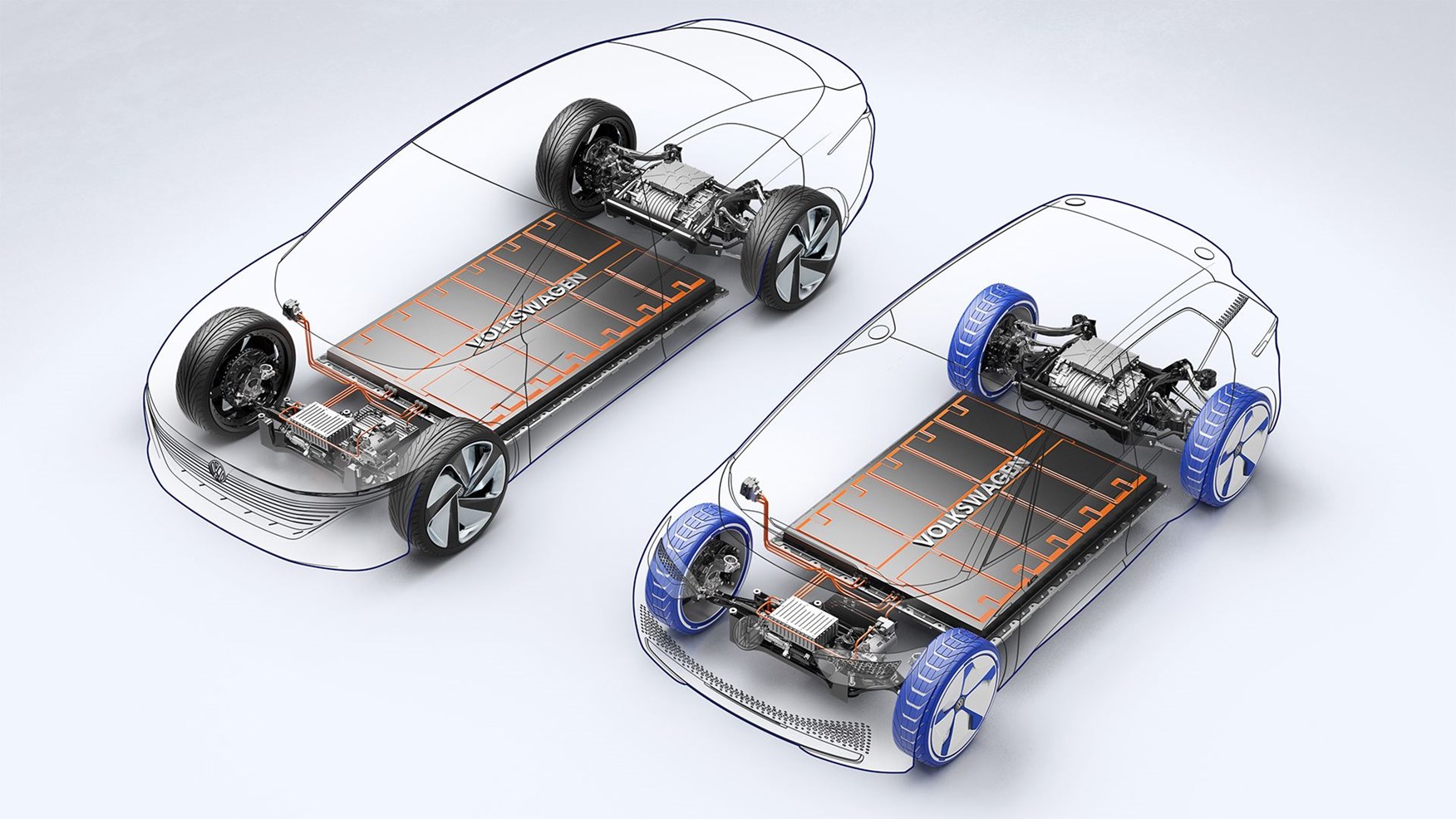
What is the capacity of an electric car battery?
The energy capacity of an electric car battery depends on many factors, including the types of batteries used and the car itself. Battery capacity is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), and the higher they are, the more miles the car can travel without recharging.
Thus, the capacity of the electric car battery ranges anywhere from 40 kWh to 200 kWh. To put that into perspective, the Tesla Model S and X has a 100 kWh battery and can go 300 miles between charges, while a Nissan Leaf has a 40 kWh battery and can go 149 miles between charges.
How long does an electric car battery last?
Many people considering purchasing one of these affordable vehicles are probably wondering how long the battery will last. After all, a car is only as good as the batteries that power it.
While high-energy car batteries don't last as long as chemicals like lithium iron phosphate, the general rule is that lithium-ion batteries in cars will last about 200,000 miles or about 17 years, which is pretty good for a battery.
A lot of battery life depends on how the battery was treated, its charge and discharge cycles, and the temperatures it operated in. Many cars use advanced battery management systems and even heating and cooling systems to keep batteries performing as intended. In the best possible way to prolong its life.
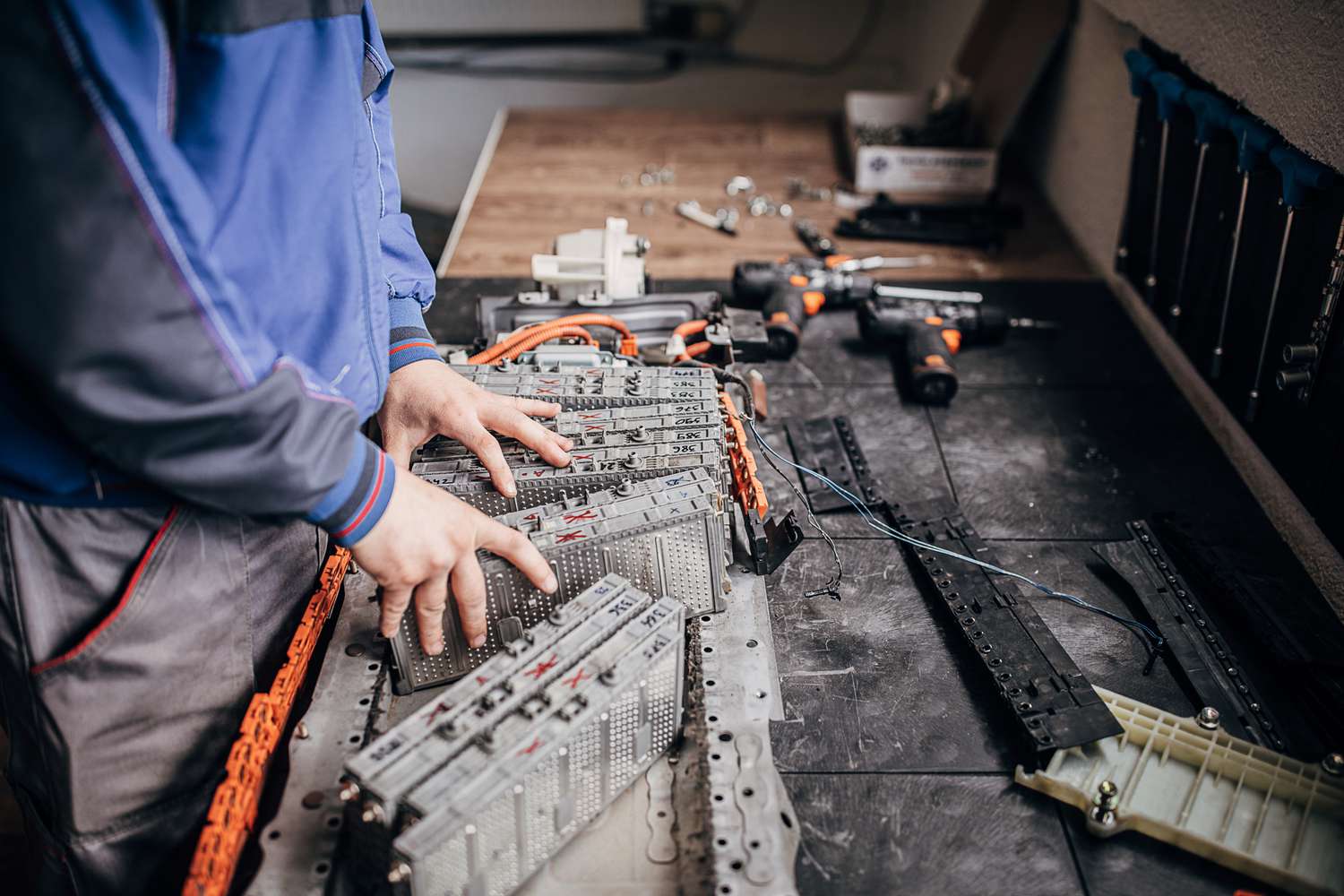

How are electric car batteries disposed of?
So, if electric car batteries eventually bite the dust, where will they all end up? In an ideal world, manufacturers would recycle them and make new batteries. This involves first shredding the batteries at dedicated facilities and then breaking them with heat or chemicals and extracting the valuable materials.
Unfortunately, we don’t live in a perfect world and only a small percentage of lithium-ion batteries get recycled. The main issue? Labor and shipping logistics. In fact, shipping these lithium-ion batteries involves more labor and resources than is required to extract new materials. Here lies the main problem: lack of profitability. However, this is currently being worked on and will be fixed as lithium batteries become the main source of power for our vehicles.
Is there any new technology in electric car batteries?
Advances in electric vehicle batteries have been ramping up and they may solve the recycling problem too.
New improvements are always being made, from energy density and production costs to safety. The ultimate goal is to make the batteries hold as much power as possible for as long as possible and as safely as possible.
Electric vehicle batteries continue to improve
Advances in batteries have come a long way and we have finally reached a point where electric cars are affordable and reliable. Lithium-ion batteries dominate this space and are likely continue to be the primary choice for many years to come.
Every battery has pros and cons, and recent developments and propositions in electric vehicle battery technology might solve many problems in the EV industry.
Also Read: Nissan to invest up to USD 575 m in Brazil to produce 2 new SUVs, 1 turbo engine
Mehul Jain
EV Specialist & Clean Mobility Advocate. Mehul Jain is an expert in India’s evolving electric vehicle ecosystem, with a focus on EVs, charging infrastructure, and sustainable mobility. His articles cover everything from government subsidies to range insights, helping readers navigate the shift to cleaner transportation.

_1772690438.webp)

_1770886465.webp)
_1716799620.webp)