Table of Content
▼- What is a Turbocharger?
- How Does a Turbocharger Work?
- Key Benefits of Turbochargers
- Drawbacks of Turbochargers
- What is a Supercharger?
- How Does a Supercharger Work?
- Key Benefits of Superchargers
- Drawbacks of Superchargers
- Turbocharger vs Supercharger: Which One is Right for You?
- Use Cases
- Turbocharger vs Supercharger – Comparison Table
- Conclusion
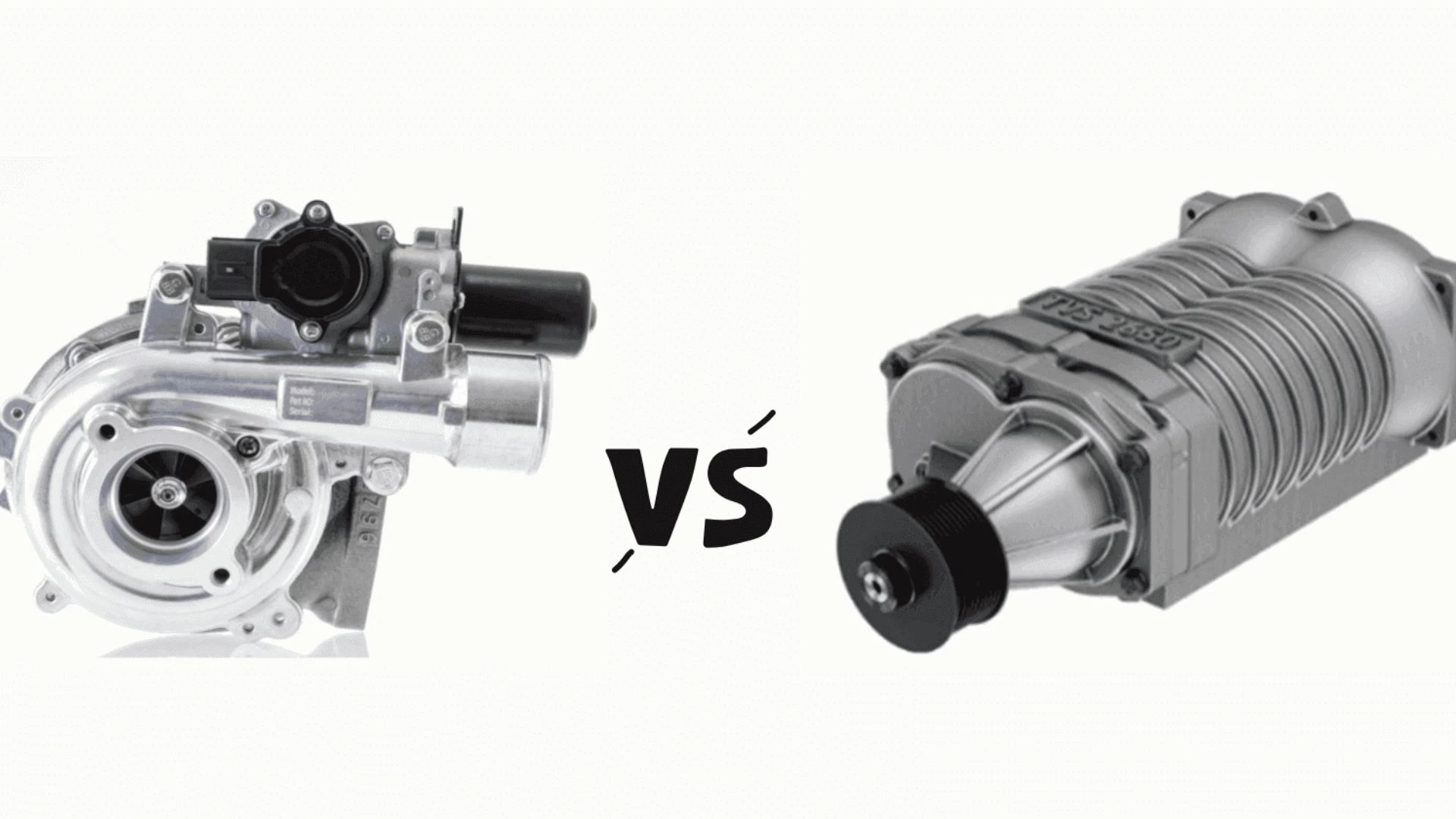
One of the more controversial subjects regarding how to extract more performance from an internal combustion engine is the turbocharger vs supercharger debate. These forced induction technologies have completely changed how engines deliver power, efficiency, and torque. But how do they differ? And which one is better for your unique driving needs?
In this thorough comparison, we will cover everything you will need to know concerning turbochargers and superchargers, including how they work, advantages, disadvantages, and which type of driver each one is suited for.
What is a Turbocharger?
A turbocharger is a forced induction tool that uses energy from exhaust gases to spin a turbine. The turbine drives a compressor to push more air into the engine and give it more fuel to make more power.
Modern engines use turbochargers because they enable more power without needing to grow the size of the engine. It takes wasted energy from exhaust gasses, so they are somewhat efficient.
How Does a Turbocharger Work?
Turbochargers consist of two main parts: the turbine and the compressor. When exhaust gases leave the engine, they pass through the turbine, causing it to spin. This spinning turbine is linked via a shaft to the compressor on the other side. As the compressor spins, it draws in ambient air, compresses it, and then sends it to the engine’s intake manifold.
This compressed air allows for more oxygen to be packed into the combustion chamber, resulting in more powerful explosions when fuel is ignited. The increased air-fuel mixture boosts engine horsepower significantly.
Key Benefits of Turbochargers
- Increased Power: Enhances performance without increasing engine size
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: Uses waste exhaust to improve combustion
- Better High-Altitude Performance: Performs well in thin air
- Lower Emissions: Cleaner burning leads to reduced pollutants
- Compact Design: Ideal for small, fuel-efficient engines
Drawbacks of Turbochargers
- Turbo Lag: A slight delay in boost response
- Complexity: More parts like intercoolers and wastegates
- Heat Generation: Higher engine temperatures
- Maintenance Costs: Needs regular checks and high-quality oils
Also Read: Bike and Car Tyre Markings Explained: Some Useful Information
What is a Supercharger?
A supercharger is also a type of forced introduction system, however, it is mechanically driven by the engine — most of the time via a belt connected to the crankshaft — rather than being dependent on exhaust gases. This means that it needs to utilize power from the engine to force more air into the combustion chamber, rather than depending on exhaust gasses.
Super chargers are famed for their immediate power delivery, making super-charged options very popular in drag racing and performance vehicles, where throttle response (or lack thereof) is important.
How Does a Supercharger Work?
The supercharger is located atop the engine and operates by mounting it directly to the crankshaft via a belt or gear train. The moment the engine starts it also spins the supercharger, which compresses air and sends it into the intake manifold.
This connection means there is no lag time - powering the engine up happens immediately, the instant you press the accelerator.
Key Benefits of Superchargers
- Instant Power: No lag—delivers immediate throttle response
- Improved Low-End Torque: Great for heavy vehicles and towing
- Simple Installation: Fewer components than turbos
- Enhanced Driving Feel: Linear power band
Drawbacks of Superchargers
- Reduced Fuel Efficiency: Consumes engine power to operate
- Increased Engine Strain: More stress on mechanical components
- No Altitude Compensation: Loses effectiveness at high altitudes
- Less Tuning Flexibility: Harder to modify compared to turbos
Turbocharger vs Supercharger: Which One is Right for You?
Now that we’ve covered both systems individually, it’s time for a head-to-head comparison. Whether you're a performance enthusiast or an everyday driver, this turbocharger vs supercharger comparison will help you choose better.
Use Cases
- Turbochargers are excellent for daily drivers who value fuel efficiency and occasional spirited driving.
- Superchargers are preferred by muscle car fans or performance seekers who want instant power.
Turbocharger vs Supercharger – Comparison Table
|
Feature |
Turbocharger |
Supercharger |
|
Power Source |
Exhaust gases |
Engine-driven (belt/gear) |
|
Boost Delivery |
Delayed (turbo lag) |
Instant |
|
Fuel Efficiency |
Higher |
Lower |
|
Installation Complexity |
High (more components) |
Moderate |
|
Cost |
Generally higher |
Slightly lower |
|
Engine Load |
Less load on engine |
Uses engine power |
|
Altitude Performance |
Performs better at high altitudes |
Decreases with altitude |
|
Emissions |
Typically lower |
Slightly higher |
|
Maintenance |
Needs more frequent service |
More durable under standard use |
|
Modification Potential |
Highly tunable |
Limited tuning options |
Conclusion
The turbocharger vs. supercharger debate is not about which is better overall; it's about which is right for your use case. For fuel economy, better emissions, or higher performance at higher altitude, obviously a turbocharger is best. Or, if you want instantaneous power and impressive driving dynamics, a supercharger is likely best.
In summary, both have unique advantages depending on your use case, your driving style, and your performance objectives.
Karan Bhatia
Karan Bhatia is an automobile expert and reviewer with 8+ years of experience test-driving cars, bikes, and EVs. He provides honest, detailed, and practical reviews that highlight performance, design, safety, and value for money. His expert insights help readers make confident choices when buying their next vehicle.


_1771411501.webp)


