Table of Content
▼The internal combustion engine generates a significant amount of heat while burning fuel to produce power. If this heat isn't properly managed, it can lead to engine overheating, posing serious risks such as fire and explosion, which endanger the driver and passengers. Overheating is one of the most hazardous engine issues that drivers must be vigilant about.

Longevity and Maintenance
Typically, a car engine requires servicing within its first five to seven years. However, some engines can run trouble-free for over a decade with proper maintenance. Regular upkeep is crucial to avoid frequent engine repairs or replacements. Despite being designed for long-term use, car engines cannot withstand extremely high temperatures for extended periods.
Consequences of Overheating
When an engine overheats, it can stop functioning altogether. High temperatures can severely damage seals and gaskets, which are essential for maintaining the engine's integrity. Overheating can cause irreversible damage, making it essential to understand its causes and how to address them promptly.
Common Causes of Engine Overheating

- Leak in the Cooling System:
A leak allows air to enter the cooling system, causing the coolant to escape and create an airlock. This air bubble can disrupt the cooling process, leading to overheating.

- Condensed Coolant:
In cold weather, low-quality coolant can freeze, creating a blockage. This prevents proper coolant flow, causing the engine to overheat and potentially damaging the radiator.
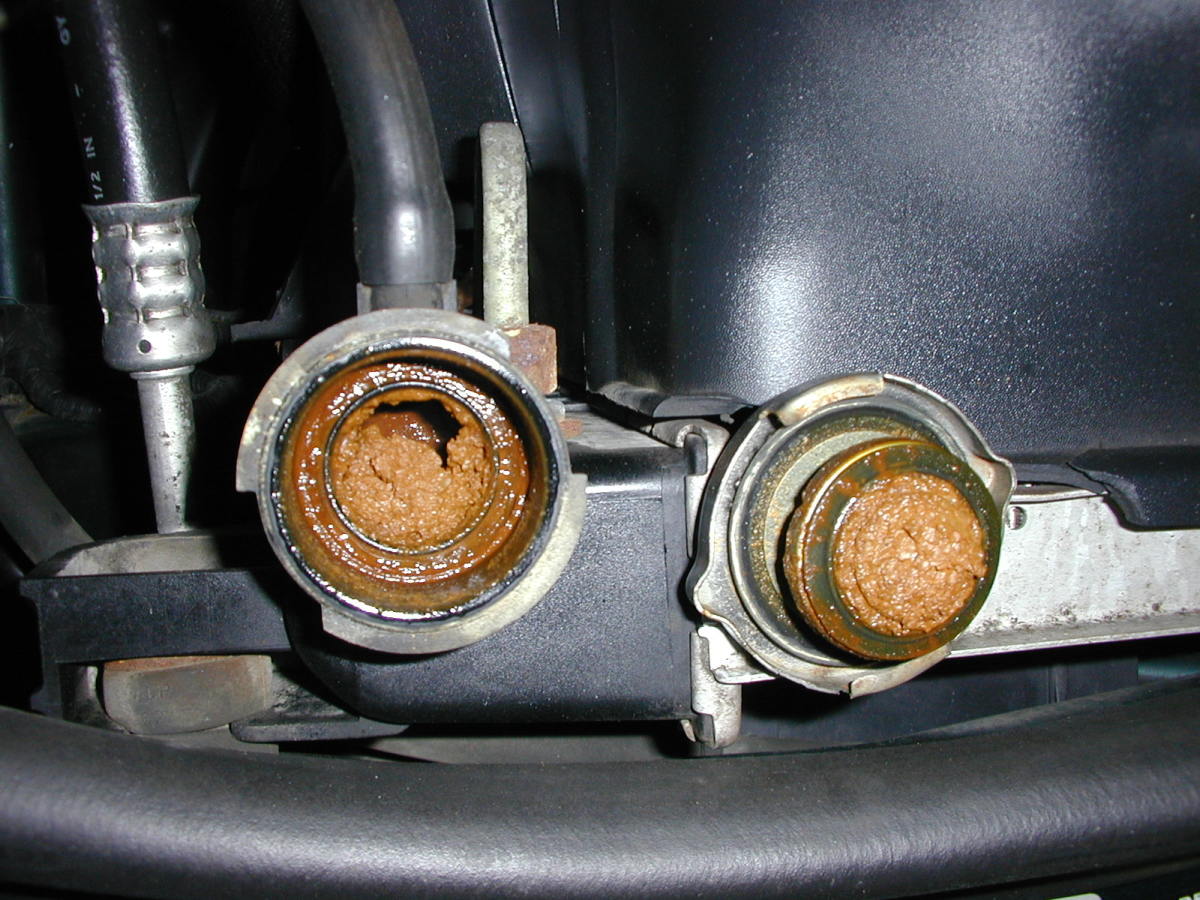

- Blockage in Coolant Circulation:
A defective thermostat, mineral deposits, or foreign objects can block coolant flow, preventing heat dissipation and causing the engine to overheat.
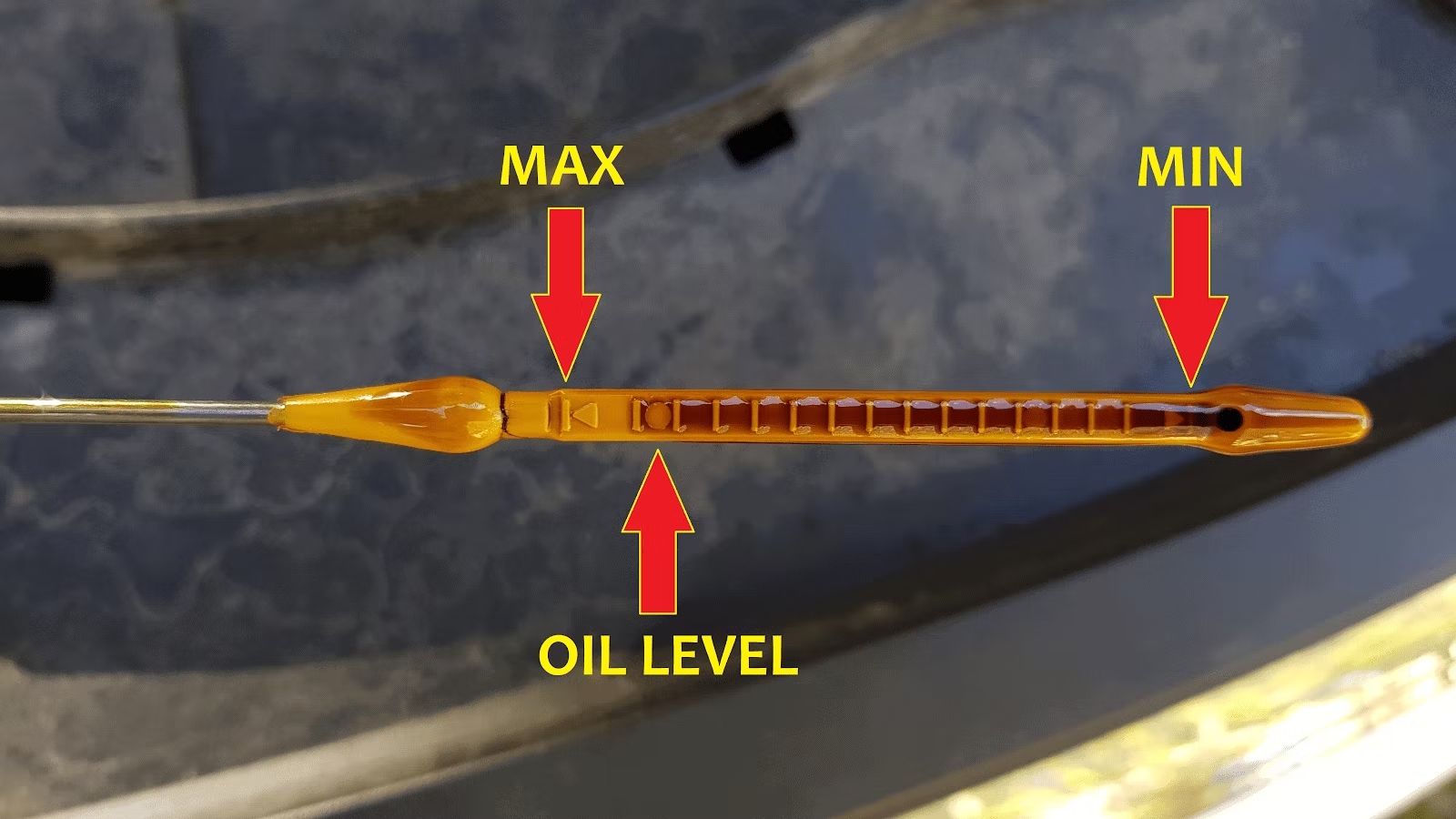

- Low Oil Level:
Engine oil helps with cooling by removing unused heat and lubricating engine parts. A low oil level can lead to excessive heat buildup and severe engine damage.
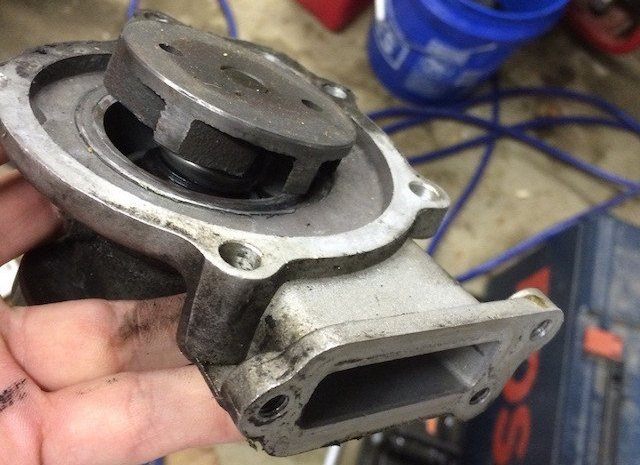

- Broken Water Pump:
The water pump is crucial for maintaining coolant circulation. If it breaks, the coolant flow stops, leading to engine overheating.
Also Read: Complete Tyre Care and Maintenance Guide
Symptoms of an Overheating Engine
- Dashboard Warnings:
The temperature gauge on your dashboard will rise to the red line or H (High) indicator when the engine overheats. Modern cars may also have a malfunction light that alerts you to overheating.
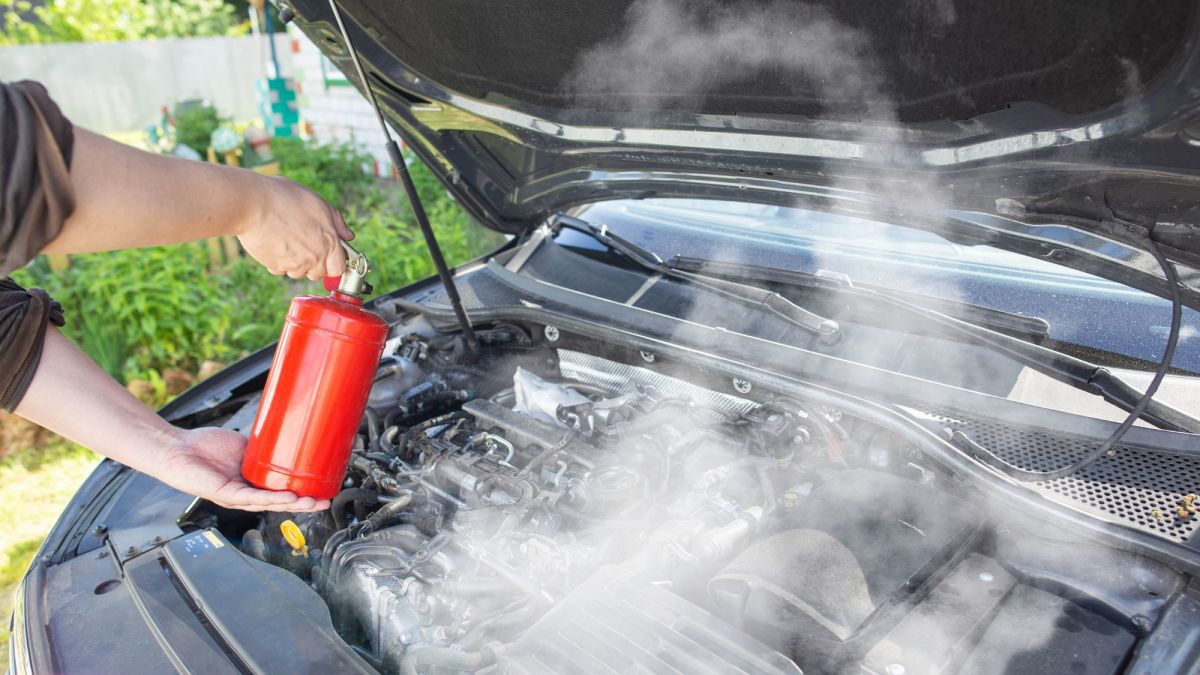
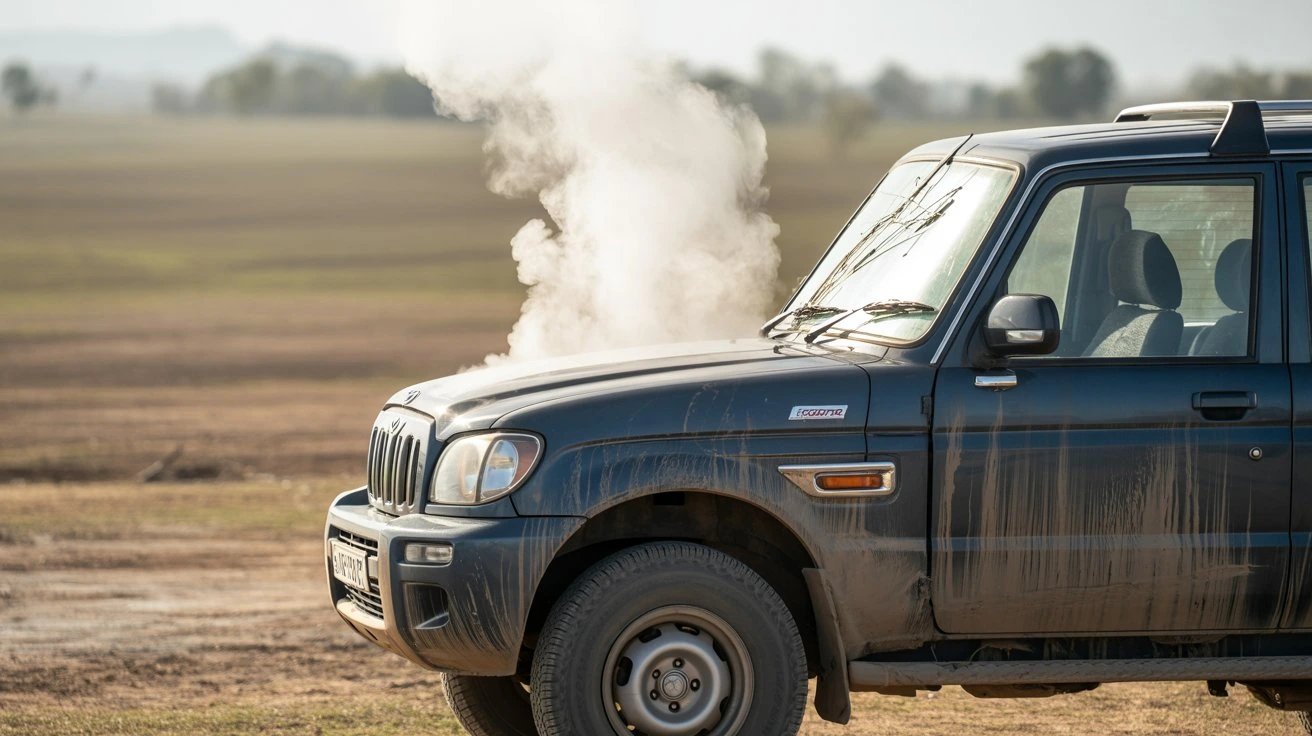
- Steam or Smoke:
If you see steam or smoke coming from under the hood, stop your car immediately. This could indicate overheating or other serious issues like oil leaks.
- Hot Air from the Air Conditioner:
Hot air from the AC may signal an impending overheating issue. Adding coolant can help mitigate this problem.
Preventive Measures
Knowing the causes of engine overheating helps you take preventive steps when a temperature issue arises. Here’s what to check:
- Coolant System: Ensure it's functioning properly without leaks or blockages.
- Engine Oil Level: Regularly check and top up the oil.
- Radiator: Inspect for blockages or damage.
- Thermostat: Make sure it’s operating correctly.
- Water Pump: Check for wear and tear.
Maintenance Tips:
- Flush the Cooling System: Clean it as recommended by the manufacturer.
- Inspect for Leaks: Regularly check the cooling system for leaks or faults.
- Oil Changes: Keep the engine oil at the correct level and change it as needed.
- Radiator, Thermostat, and Water Pump: Regularly inspect these components for any damage.
If you notice signs of engine overheating, such as the temperature gauge rising, immediately turn off the air conditioning or heating system to reduce the engine temperature. Pull over safely, turn off the engine, and inspect the engine and cooling system.
By understanding the causes and taking proactive steps, you can prevent engine overheating and ensure your vehicle runs smoothly and safely.
Also Read: Top 5 Most Affordable Electric Vehicles in India 2024



_1771411501.webp)



