_1742980666.webp)
Table of Content
▼- Key Highlights of Delhi EV Policy 2.0
- 1. Phased Transition to Electric Vehicles
- 2. Purchase Incentives for EV Adoption
- 3. Focus on Fleet Electrification
- 4. Scrapping and Retrofitting Incentives
- Delhi EV Policy 2.0 and Charging Infrastructure
- 1. Public EV Charging Expansion
- 2. Mandatory Charging Points in New Buildings
- Impact of Delhi EV Policy 2.0 on Electric Mobility
- Boost in EV Sales
- Cleaner Air and Reduced Pollution
- Job Creation and Economic Growth
- Model for Other States
- Conclusion
The Delhi government is set to introduce the Delhi EV Policy 2.0 in April 2025, aiming to revolutionize the electric vehicle (EV) landscape in the national capital. This updated policy will replace the 2020 Delhi EV Policy, which expired in August 2024 but was extended multiple times.
With a vision of achieving 95% EV adoption by 2027, the Delhi EV Policy 2.0 will focus on demand generation, infrastructure development, and stricter regulations. Let’s explore the key highlights and expected impact of this ambitious policy.
Key Highlights of Delhi EV Policy 2.0
1. Phased Transition to Electric Vehicles
- The Delhi government aims to replace all CNG auto-rickshaws, taxis, and light commercial vehicles (older than 10 years) with electric vehicles (EVs) in a phased manner.
- A full transition to electric buses is also on the agenda, reducing pollution and promoting clean mobility.
2. Purchase Incentives for EV Adoption
To encourage EV adoption, the Delhi EV Policy 2.0 will introduce attractive purchase incentives for:
- Electric two-wheelers
- Electric three-wheeler
- Electric light commercial vehicles (e-LCVs)
- Electric trucks
These incentives aim to make EVs more affordable and attractive for both individuals and businesses.
3. Focus on Fleet Electrification
- The policy emphasizes the electrification of commercial fleets, ensuring that cab aggregators, delivery services, and transport operators switch to zero-emission vehicles.
- Stricter regulatory measures will be implemented to ensure compliance with fleet electrification targets.
4. Scrapping and Retrofitting Incentives
- Vehicle owners will be encouraged to switch to EVs through scrapping incentives for old internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles.
- Retrofitting incentives will be introduced for those who wish to convert their existing petrol or diesel vehicles into electric vehicles.
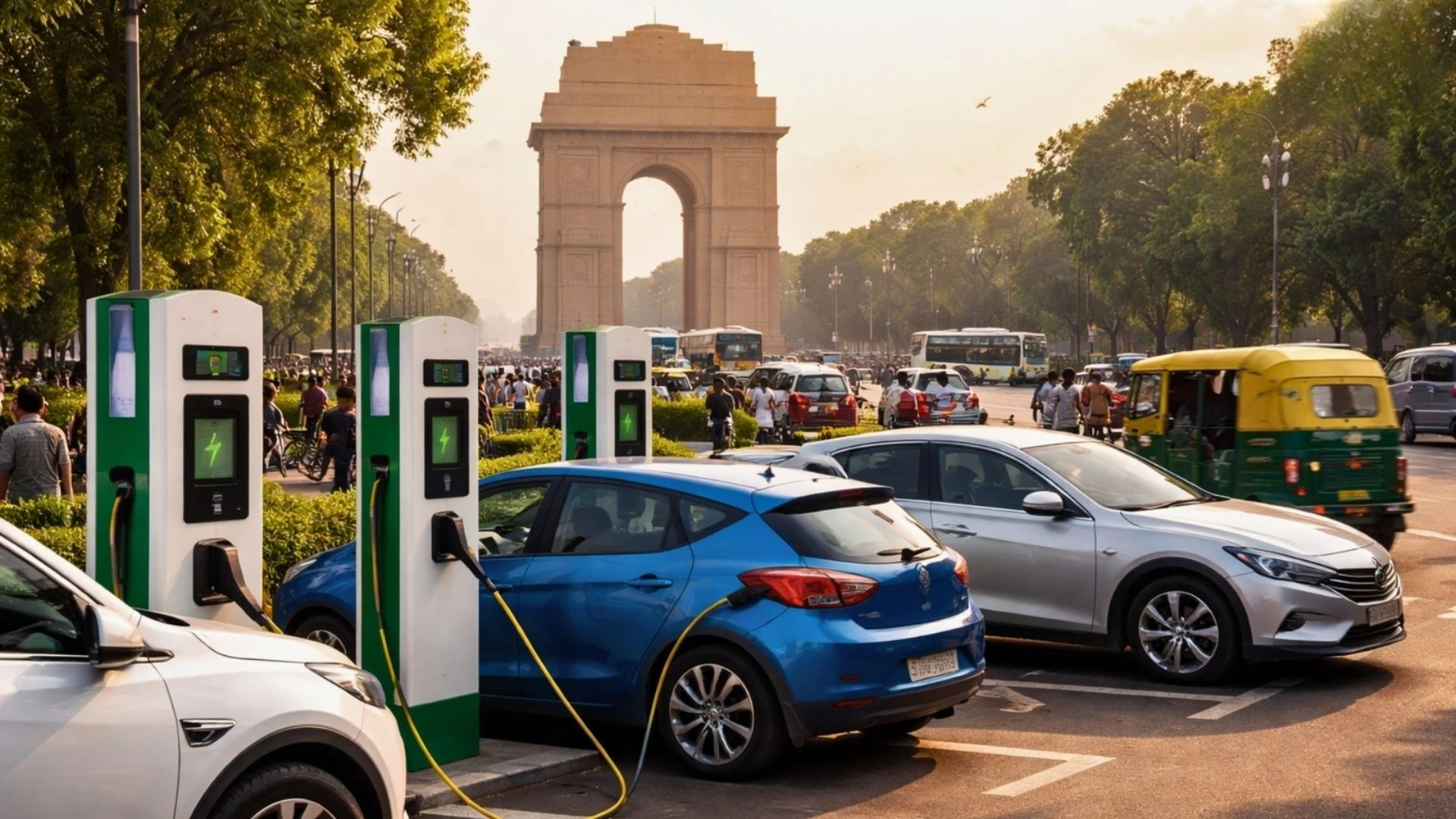
Delhi EV Policy 2.0 and Charging Infrastructure
A major focus of Delhi EV Policy 2.0 is to expand and strengthen charging infrastructure across the capital. The key initiatives include:
1. Public EV Charging Expansion
- More EV charging points will be installed across the city to improve accessibility.
- New charging stations will be set up at public places, metro stations, and highways.
2. Mandatory Charging Points in New Buildings
- New buildings in Delhi will be required to provide EV charging points for at least 20% of parking spaces.
- Older buildings must allocate at least 5% of total parking space for EV charging.
These measures will make charging convenient and encourage more people to switch to EVs.
Impact of Delhi EV Policy 2.0 on Electric Mobility
-
Boost in EV Sales
With attractive incentives and better infrastructure, the adoption of electric vehicles is expected to surge.
-
Cleaner Air and Reduced Pollution
Replacing older CNG and diesel vehicles with EVs will significantly reduce carbon emissions, improving air quality in Delhi.
-
Job Creation and Economic Growth
The demand for EVs and charging infrastructure will create new business opportunities and jobs in the automobile and energy sectors.
-
Model for Other States
Delhi’s leadership in EV adoption could inspire other Indian states to implement similar policies, accelerating nationwide EV transition.
Conclusion
The Delhi EV Policy 2.0 is a bold step towards making Delhi a leader in electric mobility. By phasing out polluting vehicles, promoting fleet electrification, and expanding charging infrastructure, the policy aims to achieve 95% EV adoption by 2027.
With the policy expected to roll out in April 2025, Delhi is set to become a model city for sustainable urban transport in India. If successfully implemented, Delhi EV Policy 2.0 could mark a significant milestone in India’s transition to clean and green mobility.
Also Read: EV Insurance Demand Surges 16x in 3 Years: A Closer Look at EV Insurance in India
Mehul Jain
EV Specialist & Clean Mobility Advocate. Mehul Jain is an expert in India’s evolving electric vehicle ecosystem, with a focus on EVs, charging infrastructure, and sustainable mobility. His articles cover everything from government subsidies to range insights, helping readers navigate the shift to cleaner transportation.


_1770886465.webp)

_1716799620.webp)