Types of Brakes: An In-Depth Guide to Modern Braking Systems
Karl Benz invented the motor car in 1885, and shortly thereafter, he must have recognized the need to stop his creation, the three-wheeled Patent-Motorwagen, which could reach speeds up to 16 kmph. Thus, by 1897, the Motorwagen was equipped with leather shoe brakes for the rear wheels to provide necessary stopping power.
Initially, wooden brakes and leather shoe brakes were common until wooden wheels were replaced by rubber ones. In 1899, Gottlieb Daimler introduced modern brakes in the form of drum brakes. Since then, braking systems have evolved significantly, and today, we have various types to choose from. Here, we explore the main types of brakes in use today.
Braking Systems
Before diving into the types of brakes, it's important to understand the different braking systems, which are primarily divided into three categories:

Mechanical Braking System
Mechanical brakes, the oldest type, were used until the 1950s. This system relied on pulleys, cables, cams, and other components to transfer friction from the brake pedal to the brakes. When the driver pressed the brake pedal, a cable would pull a brake line, activating the brakes on the wheel. However, over time, this system proved unreliable due to the wear and tear of its many moving parts and issues with brake force and precision, leading to its eventual replacement.
Hydraulic Braking System
The hydraulic braking system replaced the mechanical system in the 1950s and remains widely used today. This system operates on the principles of hydraulics, using a non-compressible brake fluid stored in a reservoir that can withstand high temperatures. Pressing the brake pedal sends pressure through brake lines to a master cylinder, which then applies pressure to the braking system on the wheels. Despite numerous advancements, the basic principle of hydraulic brakes remains the same.
Brake-By-Wire System
The most modern type of braking system is the brake-by-wire system, which eliminates mechanical or hydraulic connections in favor of electronic signals. When the brake pedal is pressed, a position sensor sends signals to activate the brakes on the wheels. This system, also known as electromechanical brakes, uses a mechanical piston and caliper setup for braking. Many electric cars today, such as the Porsche Taycan, utilize this system.
Types of Brakes
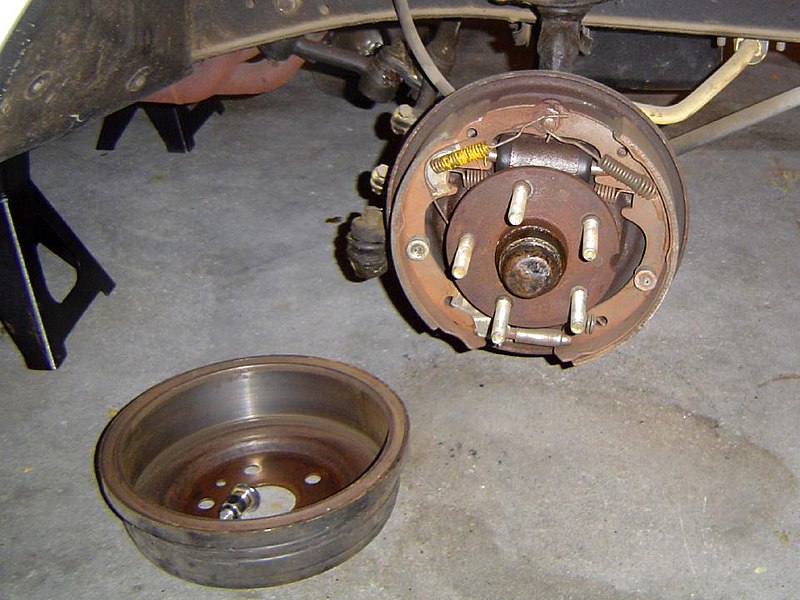

Drum Brakes
Drum brakes are one of the oldest types and consist of a drum attached to the wheel. Inside the drum are brake shoes that press against its inner surface to create friction and slow the vehicle. Drum brakes generate significant heat and, while once popular, are increasingly being replaced by more advanced alternatives.
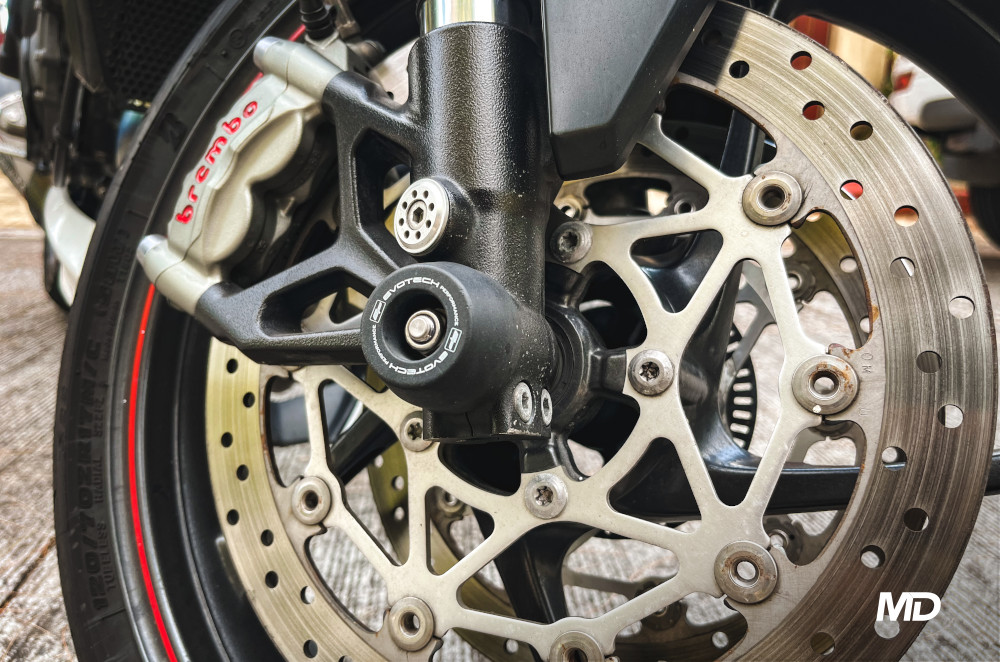

Disc Brakes
Invented in 1902 by Birmingham engineer William Lanchester, disc brakes replaced drum brakes. They feature steel discs paired with a caliper housing brake pads. When the brake is applied, hydraulic or electric pressure forces the pads against the discs, slowing the vehicle. Disc brakes are crucial to modern automotive safety and have seen many improvements, including the use of materials like carbon ceramics for better thermal management and variations like slotted and drilled discs for improved heat dissipation and reduced brake fade.

Parking Brake/Handbrake
The parking brake, or handbrake, is a secondary system used to keep a vehicle stationary during parking, especially on inclines. This system operates independently of the main braking system. Manual parking brakes use a cable system to activate drums or discs, while modern cars often feature electronic parking brakes based on brake-by-wire technology.
Popular Modern Braking Features
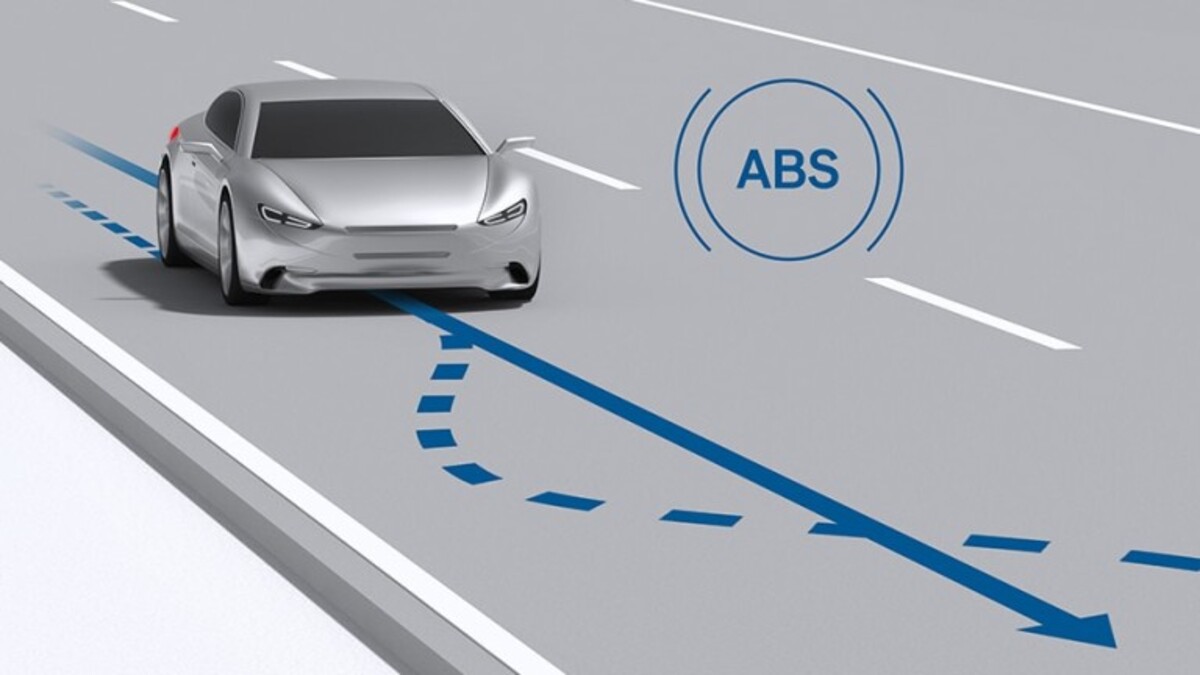
Anti-Lock Brakes (ABS)
ABS is a critical automotive safety feature designed to prevent wheel lock-up during sudden braking, allowing the driver to maintain steering control. This system is particularly effective on wet or slippery roads. ABS uses wheel speed sensors connected to an ABS pump to modulate brake force intermittently, preventing traction loss.
Summary
Automotive braking systems have significantly evolved, combining hydraulic brakes, disc brakes, and anti-lock brakes to provide superior braking performance. Regular maintenance, including inspecting brake pads and discs at manufacturer-recommended intervals, is essential for reliable brake function. Ultimately, safe driving practices, including adhering to speed limits and road rules, are crucial for safe motoring.
FAQs: Types of Brakes
Q: What are the main types of brakes used in vehicles today?
A: The main types of brakes used in vehicles today are drum brakes, disc brakes, and brake-by-wire systems.
Q: What types of brakes are used in modern electric vehicles?
A: Modern electric vehicles often use brake-by-wire systems, which rely on electronic signals to activate the braking mechanism, providing more precise control and integration with regenerative braking systems.
Q: What type of brakes are typically used for parking brakes?
A: Parking brakes, or handbrakes, can use either mechanical systems with cables or modern electronic parking brakes that work on the brake-by-wire principle.
Q: What types of brakes are most common in high-performance vehicles?
A: High-performance vehicles typically use advanced disc brakes with larger discs and multiple-piston calipers, often made from materials like carbon ceramics for better thermal management and braking performance.
Q: How do drum brakes differ from disc brakes?
A: Drum brakes use a drum attached to the wheel and brake shoes that press against the drum's inner surface to create friction. Disc brakes use steel discs paired with calipers that house brake pads, which press against the discs to slow the vehicle.
Also Read: Signs Your Car's Brakes Need Inspection: Don't Overlook These Warning Signals